With 5G networks still rolling out across the globe, talk of 6G might seem premature—but make no mistake: the race to develop the next generation of wireless communication is already well underway. While 5G promised (and is delivering) faster speeds and lower latency, 6G aims to revolutionize connectivity, merging the physical and digital worlds in ways we’ve only begun to imagine.
So, is 6G really coming? What does it mean, and when can we expect it? Here’s what you need to know about what comes after 5G.
What Exactly Is 6G?

6G stands for sixth-generation wireless technology, the successor to 5G. While 5G brought gigabit speeds and ultra-low latency, 6G is expected to push these capabilities exponentially further, enabling futuristic applications such as:
- Holographic communications
- Fully immersive AR/VR experiences
- Real-time remote surgeries
- Autonomous drone swarms
- AI-powered smart cities
The overarching goal? To create an intelligent, hyperconnected network that supports real-time data transfer, sensing, and computation at unprecedented scale and speed.
How Fast Will 6G Be?

While 5G can reach speeds of up to 10 Gbps, 6G is expected to hit 100 Gbps or more, with latency potentially as low as 100 microseconds (vs. 1 millisecond for 5G). This would make 6G networks about 100 times faster and 10 times more responsive than current 5G networks.
But 6G isn’t just about raw speed—it’s about intelligent connectivity that enables devices to communicate, analyze, and act in real time.
Key Features of 6G
1. Terahertz Frequencies
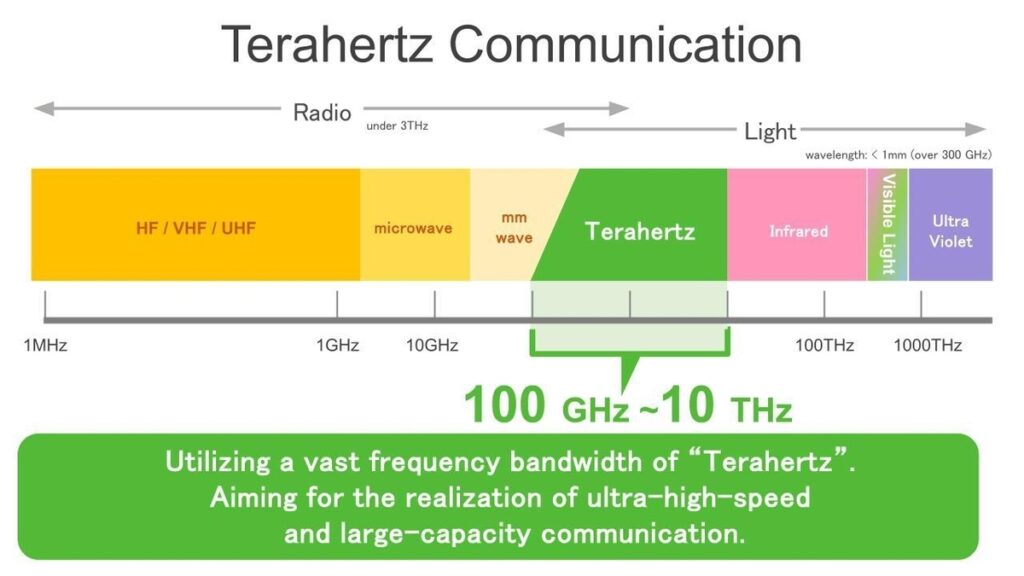
6G will likely operate in the terahertz (THz) spectrum—frequencies above 100 GHz, far beyond what 5G uses. These frequencies can carry massive amounts of data but have very short range and poor penetration through obstacles, meaning denser infrastructure (like micro base stations) will be needed.
2. AI-Native Networks
6G will integrate AI at the core of its architecture—not just for devices, but for managing networks themselves. AI will optimize traffic, improve security, and even predict failures before they happen.
3. Massive Device Density
While 5G supports about 1 million devices per square kilometer, 6G could handle 10 million or more, enabling the full realization of smart cities, intelligent factories, and massive IoT ecosystems.
4. Holographic and XR Communications
6G is expected to deliver the bandwidth and latency needed to make real-time holograms and extended reality (XR) experiences common in everyday communications, education, entertainment, and remote work.
5. Sensing-as-a-Service
6G will also double as a sensing network. Devices won’t just communicate—they’ll act as environmental sensors, mapping terrain, detecting movement, and even reading health metrics non-invasively.
Why Do We Need 6G?
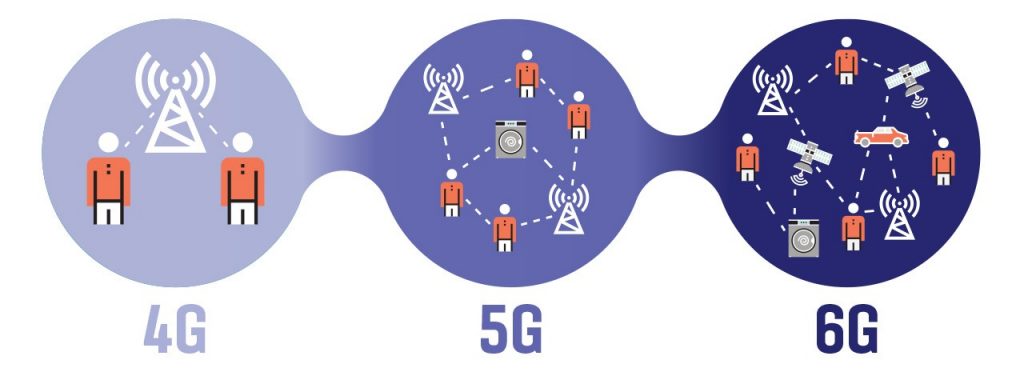
While 5G is transforming connectivity in areas like autonomous vehicles, cloud gaming, and remote work, next-gen applications will need even faster, more reliable, and more intelligent networks. Here’s why:
- Immersive tech (AR/VR/XR) requires ultra-low latency and high throughput.
- Autonomous machines need near-instant communication for safety and coordination.
- Remote health services, like surgeries or diagnostics, require extreme precision and reliability.
- AI and edge computing will demand real-time, location-specific data transfer and processing.
Put simply: as our tech becomes more immersive, mobile, and interconnected, 5G won’t be enough.
When Will 6G Arrive?
Most experts agree that 6G won’t be commercially available until around 2030. But the groundwork is already being laid:
Current Timeline:
- 2020–2023: Early research and standard proposals (universities, private labs, government programs).
- 2024–2027: Prototypes, early trials, spectrum regulation.
- 2028–2030: Finalization of global standards.
- 2030 onward: Commercial rollout in select regions, gradual global adoption.
Global Investment:
- China, South Korea, Japan, the U.S., and the EU are all heavily investing in 6G research.
- Companies like Samsung, Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, and Qualcomm are key players in shaping the 6G landscape.
- The Next G Alliance in North America is working to ensure leadership in future wireless innovations.
What Will 6G Enable?
Here are some real-world use cases that 6G could make possible:
1. Digital Twins of Cities
Imagine a fully synchronized, real-time virtual model of an entire city, used for disaster response, traffic management, or infrastructure planning. 6G’s bandwidth and latency make this possible.
2. Mind-Computer Interfaces
Neural devices may allow users to interact with digital systems using thoughts, supported by ultra-fast, brain-compatible data transfer. While early-stage, this is a major long-term goal.
3. Global Connectivity via Satellite-6G Integration
6G will likely merge with non-terrestrial networks—like LEO satellites (e.g., Starlink)—to provide high-speed connectivity anywhere, even in remote or underserved regions.
4. Autonomous Everything
From delivery drones to robot assistants to self-driving cars, 6G will offer the instantaneous communication and coordination needed for seamless autonomy.
Challenges to Overcome

While 6G sounds promising, there are major hurdles to clear:
1. Technical Feasibility
Terahertz waves offer incredible bandwidth but come with limitations like short range and signal degradation. Engineering viable devices and infrastructure is a major challenge.
2. Infrastructure Overhaul
6G will require an even denser network of antennas, base stations, and edge computing centers than 5G—which means massive investment and regulatory coordination.
3. Energy Efficiency
Faster speeds mean more power consumption. To scale sustainably, 6G networks will need to prioritize green tech and energy optimization.
4. Standardization and Spectrum Allocation
Global coordination on standards, spectrum use, and interoperability is essential—but also notoriously complex and politically fraught.
5G vs. 6G: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | 5G | 6G (Projected) |
|---|---|---|
| Max Speed | ~10 Gbps | 100 Gbps+ |
| Latency | ~1 ms | ~100 microseconds |
| Device Density | ~1 million/km² | 10+ million/km² |
| Frequency Range | Up to ~100 GHz | 100 GHz – 1 THz |
| AI Integration | Partial | Core to network function |
| Commercial Availability | 2019–2025 | ~2030 |
Final Thoughts: A More Connected Future
So, is 6G coming? Absolutely. Though we’re still years away from using it in our daily lives, 6G is already in development and shaping the future of connectivity.
It’s not just an upgrade—it’s a reimagining of what wireless networks can be: ultra-fast, intelligent, immersive, and omnipresent. As technology advances and our digital needs grow, 6G will be the foundation for everything from autonomous cities to immersive learning and health care without borders.
Until then, 5G will continue to expand its reach and capabilities—but 6G is already on the horizon, promising a future where the line between physical and digital disappears entirely.




