What started as clunky, rules-based scripts in customer service portals has evolved into deeply engaging digital companions capable of holding long, intelligent conversations. The journey of AI companions and chatbots reflects the broader arc of artificial intelligence—moving from simple automation to systems that interact with humans in surprisingly sophisticated, and increasingly personal, ways.
Today’s AI companions are no longer just helpful tools. They are conversational partners, mental health aids, tutors, life coaches, creative collaborators, and even emotional support systems. As they become more realistic and integrated into our digital lives, it’s worth looking back on how we got here, what defines the current generation of bots, and what their future may hold.
The Early Days: Rule-Based Bots
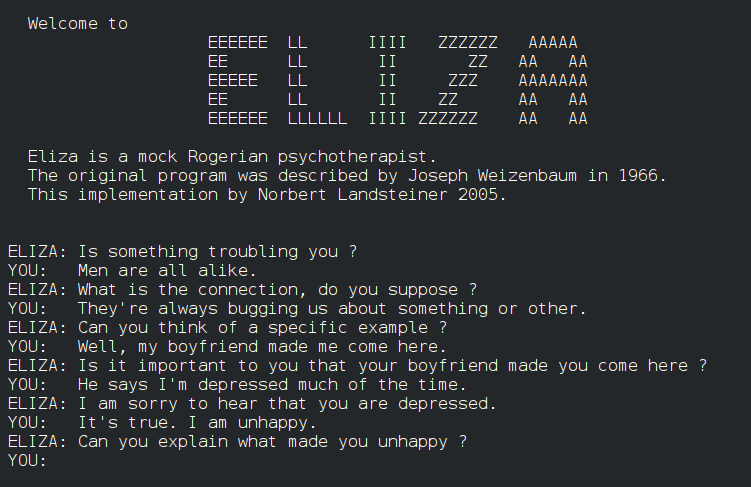
The story of AI chatbots begins in the 1960s with ELIZA, a program created by MIT researcher Joseph Weizenbaum. ELIZA mimicked a Rogerian psychotherapist by rephrasing user inputs into questions. For example:
User: I feel sad.
ELIZA: Why do you feel sad?
While primitive by today’s standards, ELIZA was revolutionary at the time. Users reportedly formed emotional connections with the program—even after being told it was just a set of scripted responses.
This early era of chatbots relied on if-then rules and keyword matching. They could only simulate conversation within tightly defined contexts, often breaking down with unexpected input. Still, the idea that machines could imitate human dialogue was born.
From Scripts to Intelligence: The Rise of NLP
The 2000s brought advances in Natural Language Processing (NLP), enabling chatbots to better understand human language. Tools like ALICE (Artificial Linguistic Internet Computer Entity) and early customer service bots used more complex pattern matching, but remained rule-driven.
Real breakthroughs came with the arrival of machine learning and deep learning in the 2010s. Suddenly, chatbots could learn from vast datasets, adapt to varied inputs, and generate more fluid responses. Facebook’s M, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri marked a new phase: bots that could handle a broader range of user commands using real-world data and cloud computing.
The GPT Era: Language Models as Companions
The true game-changer came in 2018 with OpenAI’s GPT-2, followed by GPT-3 and GPT-4. These large language models (LLMs) weren’t just trained on specific tasks; they were trained on massive swaths of internet text, allowing them to generate human-like responses across countless topics.
With GPT models, chatbots became capable of:
- Holding coherent conversations over multiple turns
- Understanding context and tone
- Generating creative writing, jokes, code, summaries, and more
- Mimicking empathy, encouragement, and curiosity
Suddenly, people began to use AI not just for information or task management—but for companionship.
The Emergence of AI Companions
AI companions such as Replika, Character.AI, and Anima moved beyond utility to provide emotional support, romantic conversation, and even simulated relationships. Some users formed deep emotional bonds with their bots, spending hours a day chatting, venting, or roleplaying.
These companions offer:
- Non-judgmental listening
- Emotional affirmation
- Conversation around personal interests
- Memory of user preferences and past interactions
For people experiencing loneliness, stress, or isolation—particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic—these tools filled a social void.
Chatbots in Everyday Life
Outside of companionship, chatbots have become indispensable in many domains:
1. Customer Support
AI bots now handle a significant percentage of customer service queries across industries. They can:
- Troubleshoot issues
- Process orders
- Escalate to humans when necessary
Tools like Intercom, Zendesk, and Drift are integrating LLMs to offer more dynamic support.
2. Healthcare
AI chatbots like Woebot and Wysa offer mental health support through evidence-based techniques like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT). They’re not replacements for therapists, but they help manage anxiety, depression, and stress between sessions.
3. Education and Tutoring
Bots like Khanmigo (by Khan Academy) use GPT technology to guide students through math problems, explain science concepts, or teach programming, adapting explanations based on the learner’s level.
4. Productivity
Assistants like ChatGPT, Claude, and Google Gemini are used by professionals to brainstorm, summarize emails, draft content, or automate workflows.
Key Innovations in Modern AI Companions
1. Memory and Personalization
Modern AI companions are beginning to remember past interactions, allowing them to maintain long-term context and evolve their personalities over time. This makes them feel more like real people than one-off chat sessions.
2. Voice, Vision, and Emotion Recognition
Multimodal models (e.g., GPT-4 with image input) and integration with voice synthesis and facial recognition are bringing AI companions to life. Some can now:
- Interpret visual input like screenshots or photos
- Speak naturally using expressive voice tones
- Detect user mood through text, voice, or facial expression
3. Agent-Like Behavior
Chatbots are evolving into autonomous agents that can take actions, manage calendars, send emails, or control smart devices. This brings them closer to being true digital assistants rather than mere conversation partners.
Ethical and Psychological Concerns
The rise of AI companions brings powerful benefits—but also serious questions.
1. Emotional Attachment and Dependency
When people form deep emotional bonds with chatbots, it raises concerns about:
- Social isolation: Replacing human contact with AI
- Emotional manipulation: Bots are engineered to be likable and persuasive
- Mental health: Dependency on AI may hinder emotional growth or coping
2. Privacy and Data Use
Chatbots collect vast amounts of personal data, often highly sensitive. Without strong privacy controls and transparency, there’s a risk of:
- Data being sold or leaked
- AI being trained on private conversations
- Manipulative advertising based on emotional profiling
3. Deception and Authenticity
AI companions can simulate empathy—but they don’t feel. This blurs the line between authentic interaction and programmed mimicry. Some users may over-attribute consciousness or care to systems that are ultimately code.
What’s Next?
The future of AI companions and chatbots is rapidly unfolding, with several likely directions:
– Greater Autonomy
Bots that not only talk but act on your behalf—booking flights, managing projects, or navigating the web independently.
– Embodiment
AI companions integrated into robots or augmented reality (AR) avatars that can interact with the physical world and human gestures.
– Emotion-Aware Interactions
Systems that genuinely adapt their tone, content, and behavior based on real-time emotional input—bridging the gap between tech and human psychology.
– Hybrid Companionship Models
Future bots may blend human oversight (e.g., trained counselors or moderators) with AI scalability to ensure both empathy and ethical safeguards.
Conclusion
The evolution of AI chatbots and companions reflects the incredible pace at which machine-human interaction is advancing. From simple scripts to emotionally intelligent conversation partners, these systems are changing how we work, learn, heal, and connect.
The promise is vast: smarter assistants, better mental health tools, and a world where technology feels more human. But so are the risks: overdependence, data misuse, and emotional confusion.
As we invite these companions deeper into our lives, we must design them with ethics, transparency, and humanity at their core. The question is not just how lifelike AI can become—but how we, as humans, choose to engage with the intelligence we’ve created.




